ACOE
The selection of renewable energy technologies is widely based on the economic index Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE). However, the LCOE ignores the potential temporal mismatch between electricity generation and actual grid demand.
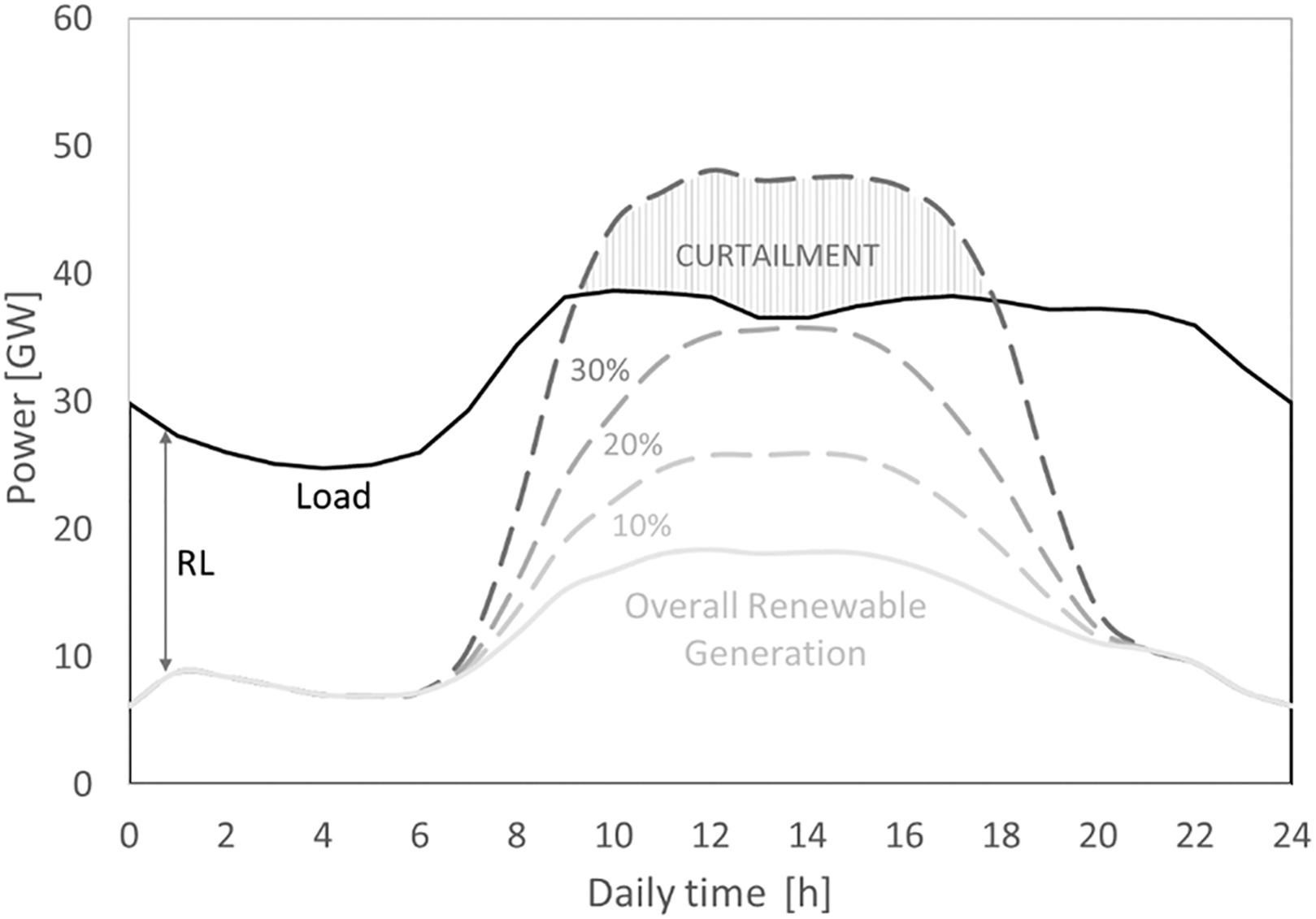
Pictures below show the importance of accounting for the grid needs when assessing the economic sustainability of a technology as some electricity might be curtailed.
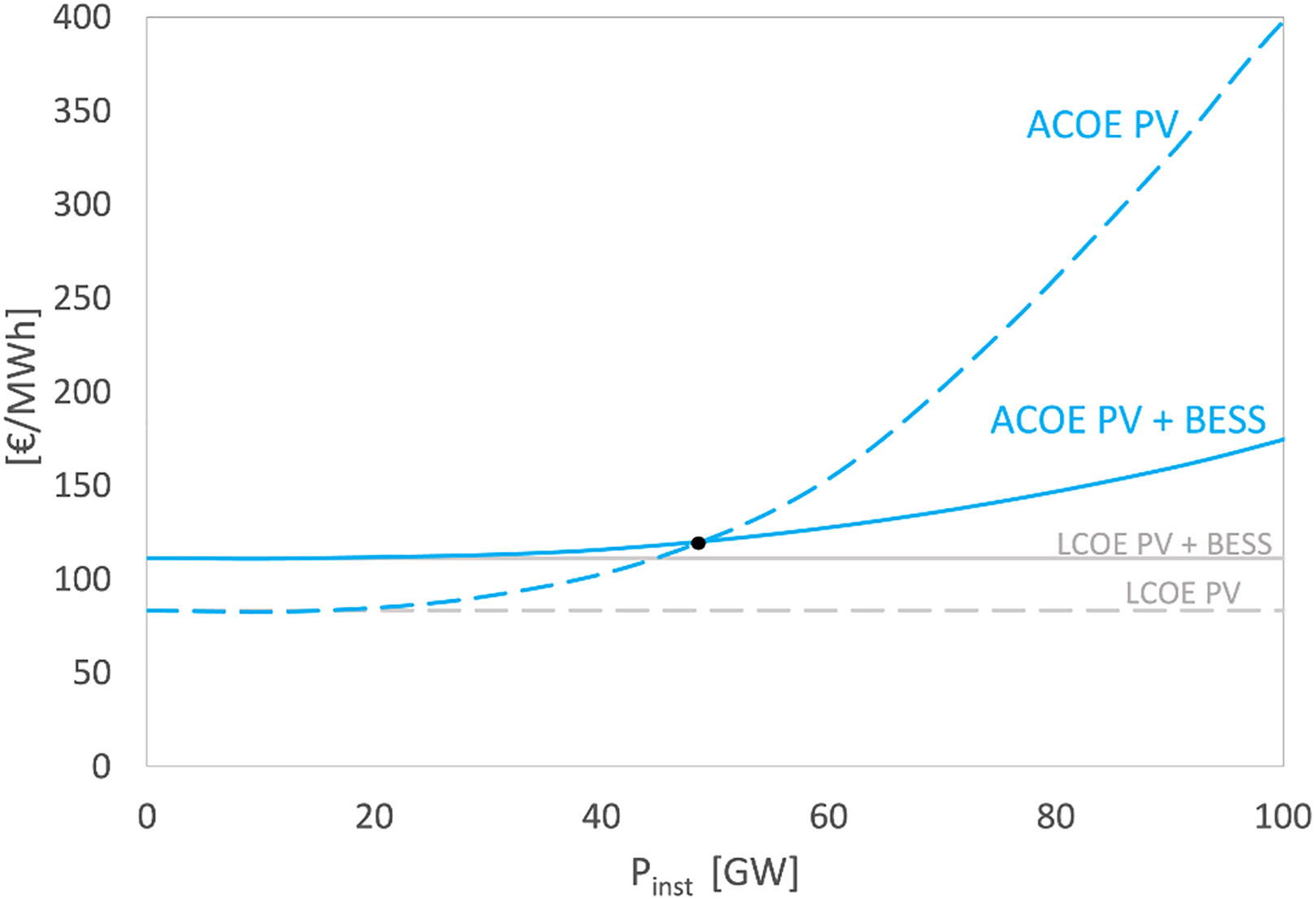
ACOE is a new economic Index introduced to estimate the potential temporal mismatch between electricity generation and actual grid demand. It allows the identification of the breakthrough conditions that make storage adoption economically feasible.
The ACOE can be calculated as follow:
\begin{cases} El_{sold}[MWh] = \sum_{i=1}^{8760} min(El_{pr,i}; RL_{i}) = \sum_{i=1}^{8760} min(P_{inst} \cdot el_{pr,i}; RL_{i}) \\ ACOE_{ P_{inst} + \Delta P } \left[ \frac{ $ } { MWh } \right] = \frac{ Cost_{ P_{inst} + \Delta P } - Cost_{ P_{inst} } } { El_{sold, P_{inst} + \Delta P } - El_{sold, P_{inst} } } \end{cases}
Where \(El_{pr,i}\) and \(RL\) are the electricity generation and the actual residual load in the \(i\)-th hour of the year, respectively.
Since \(El_{sold}\) strongly depends on the installed capacity (\(P_{inst}\)), ACOE is calculated as the incremental cost to install new capacity (\(\Delta P\)) divided by the incremental electricity sold.
Specific description of ACOE Methodology and calculation can be found in the Article available on IScience Cell Press Journal website: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.109897